MariaDB Database Server Cloning
XLServer provides advanced cloning capabilities for MariaDB database servers, allowing teams to quickly provision test, QA, development, and troubleshooting environments.
Two types of clones are supported:
- Virtual Clone: Lightweight, snapshot-based, minimal storage, very fast.
- Physical Clone: Full database duplication, independent instance, slower to provision.
From XLServer, a virtual clone can be converted into a physical clone at any time.
⚙️ Prerequisites
Before creating MariaDB clones, ensure:
- XLServer has SSH access to the target host.
- Target environment is already added to XLServer.
- Target environment is compatible with the source:
- Same Linux architecture.
- Same distribution and major version.
- Target MariaDB binary must be equal or higher than source version.
- Target MariaDB hosts must have NFS client installed.
🌀 Clone Types
Virtual Clone
- Created using snapshot technology.
- Very fast (typically < 30s).
- Requires minimal disk space.
- Supports reset, share, convert-to-physical, start, stop.
Physical Clone
- Full copy of source MariaDB database server.
- Requires disk space equal to the source.
- Slower to provision (size-dependent).
- Behaves as a completely independent instance.
🌐 Create MariaDB Virtual Clone
-
Open MariaDB server detail page.
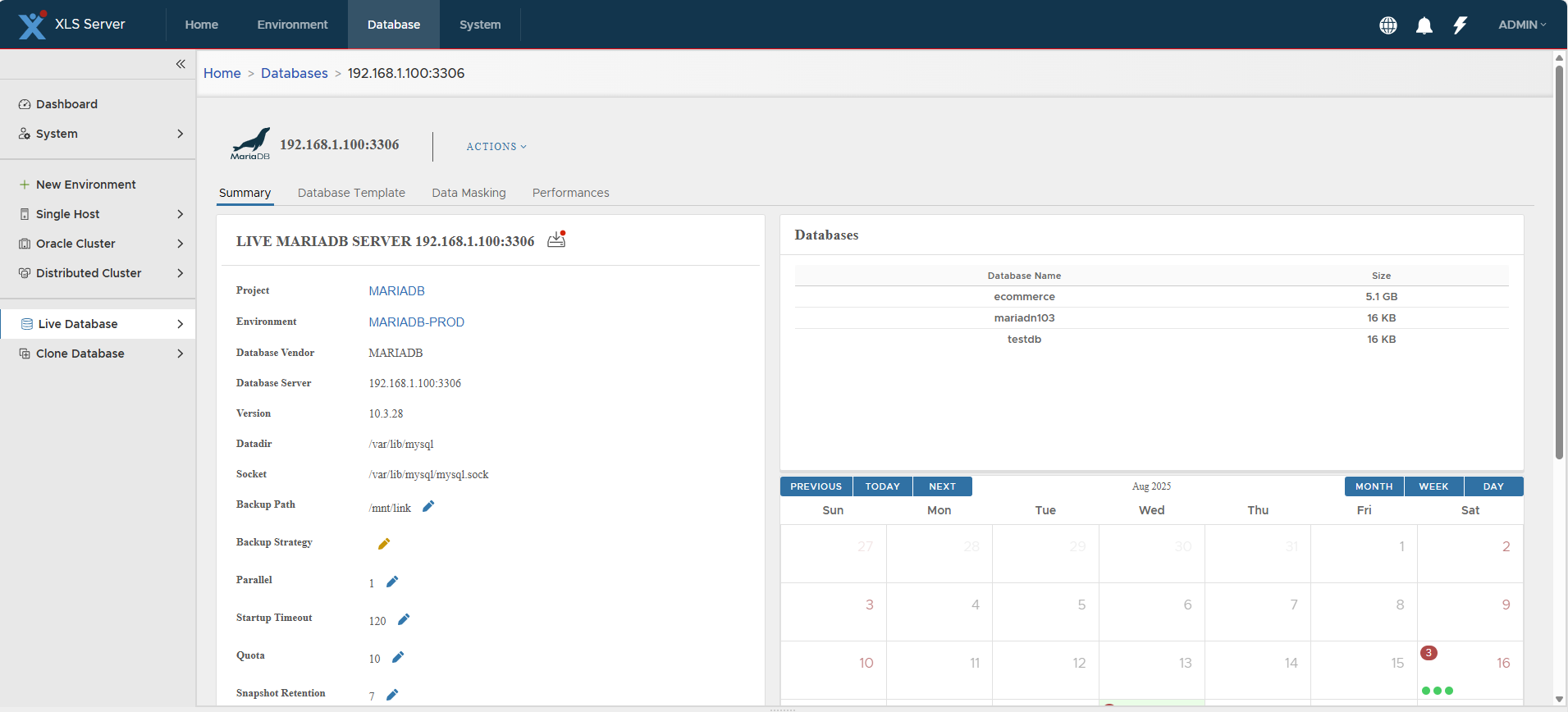
-
Click Actions > Create Virtual Clone → Confirm.
-
The Cloning Wizard is displayed.
-
Select the Target Environment → Next.
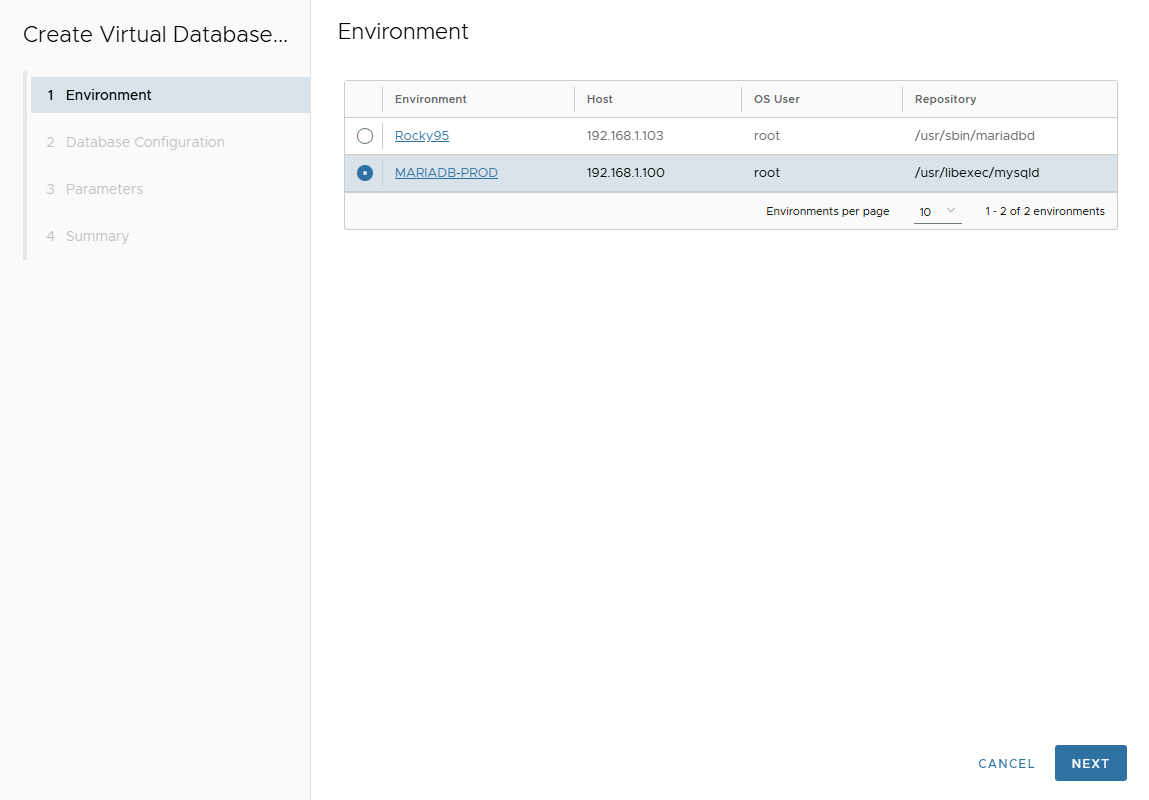
-
On Database Configuration page, provide:
- Port Number
- Mount Base (NFS mount point)
- Parallel threads (for restore or SQL execution parallelism)
- Post Script Path (optional SQL script after clone creation)
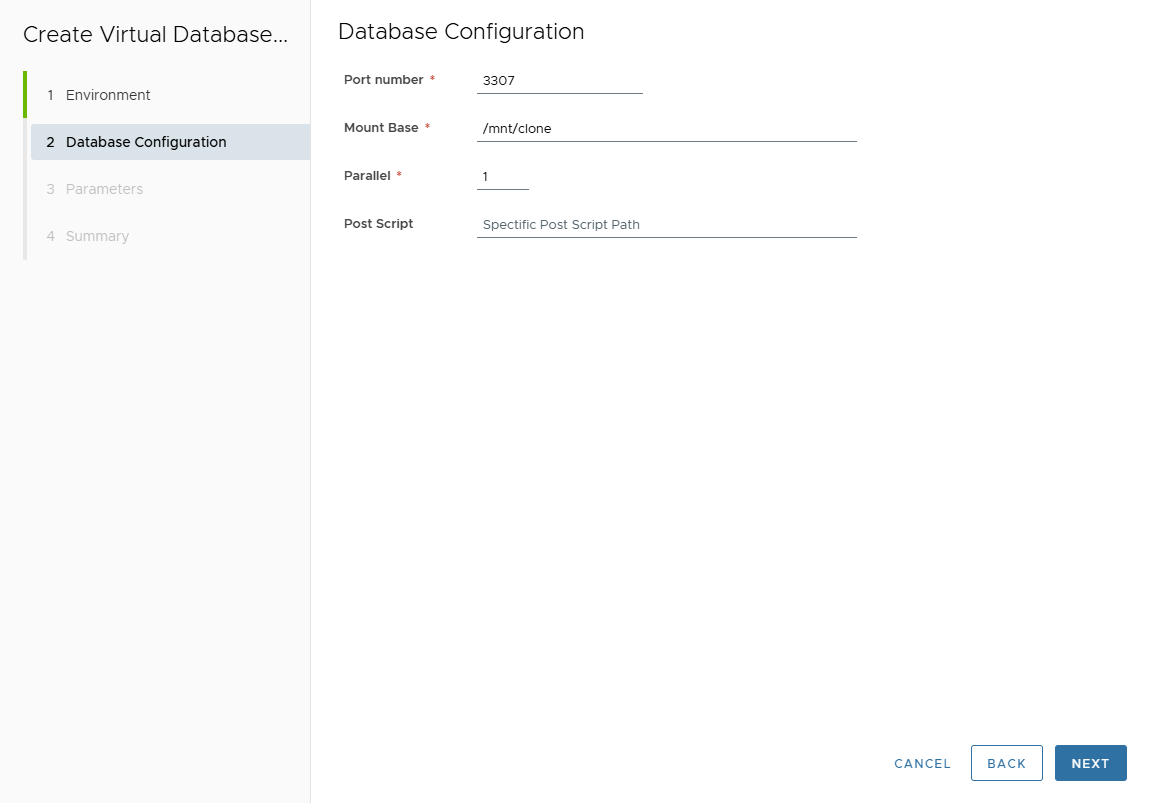
Click Next.
-
On Parameters page, adjust clone parameters if necessary.
Values are inherited from attached template or source DB.
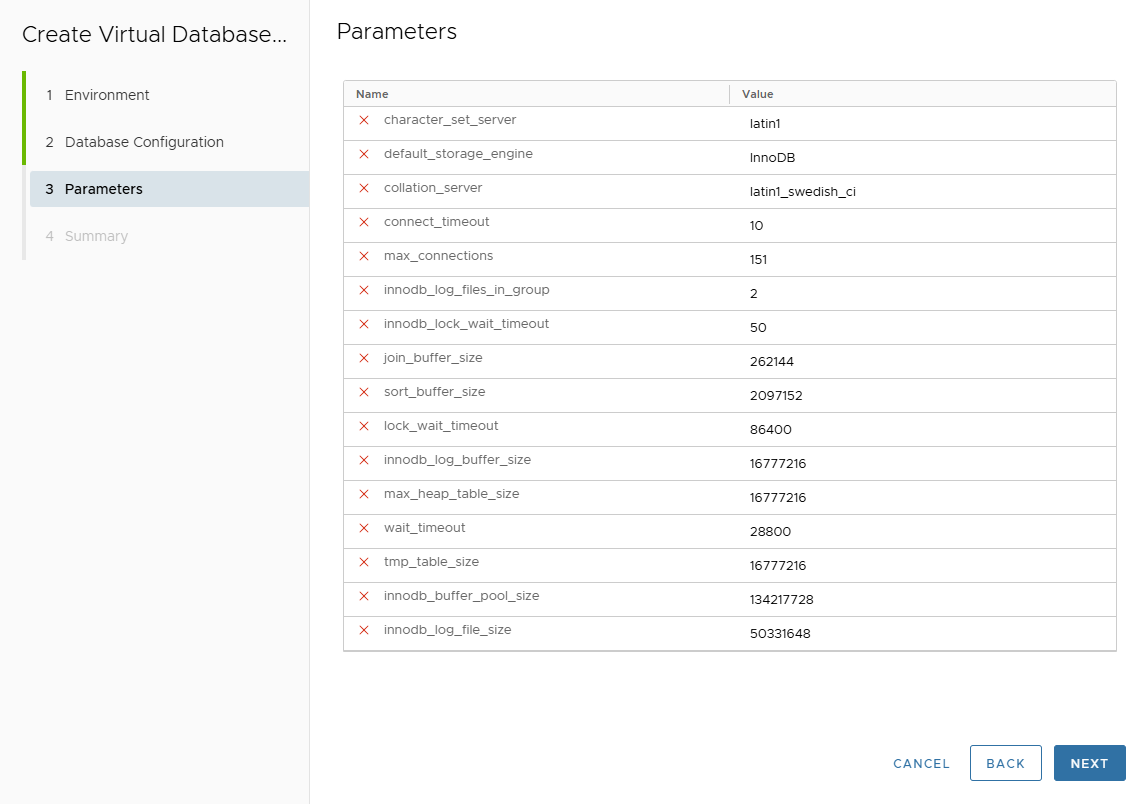
Click Next.
-
Review the Summary page.
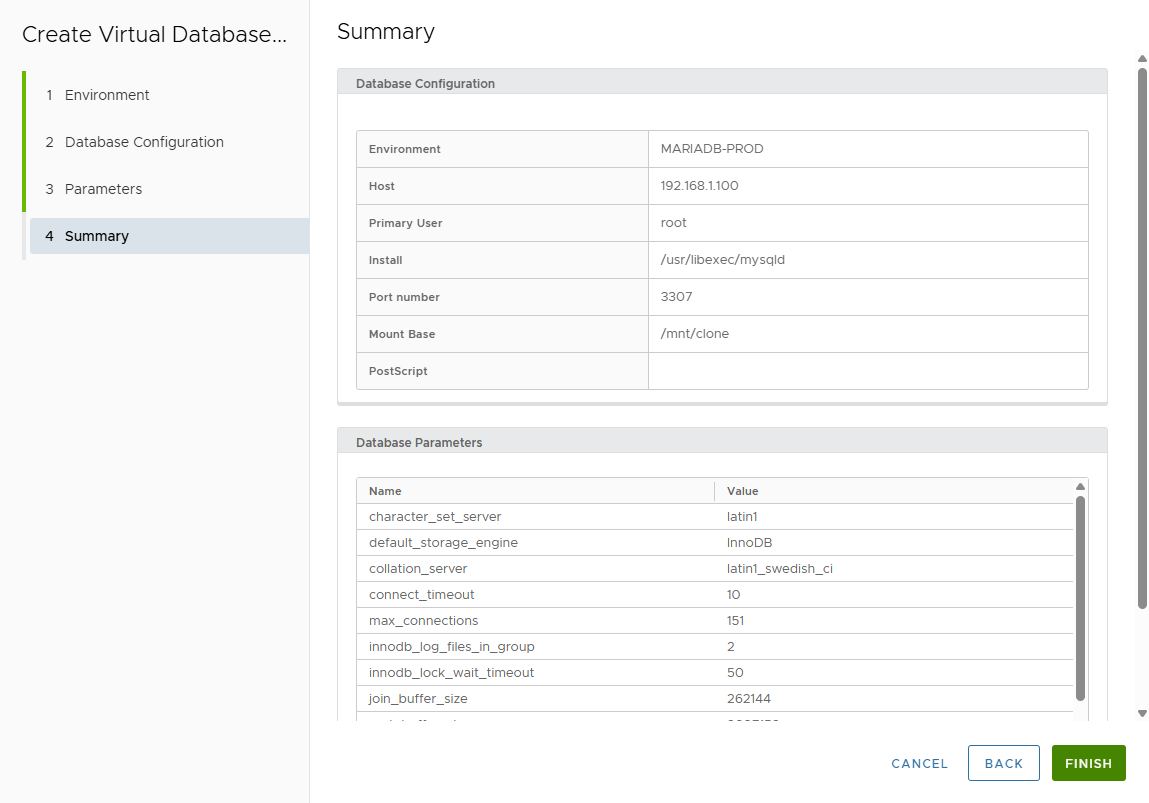
-
Click FINISH.
-
Track job execution in the Job list.
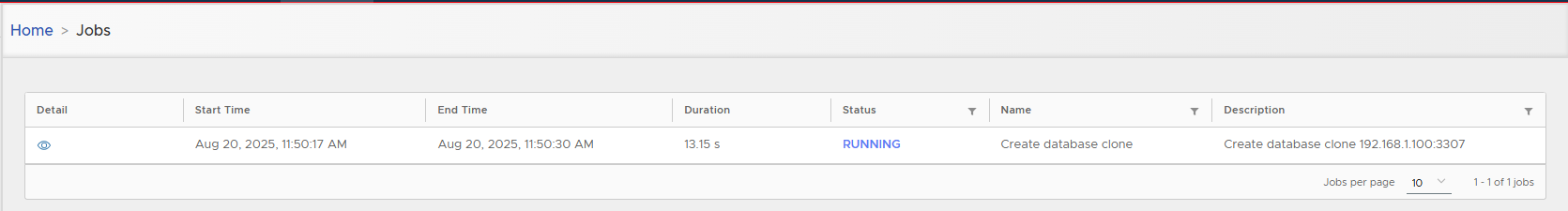
-
Open the Virtual Clone detail page.
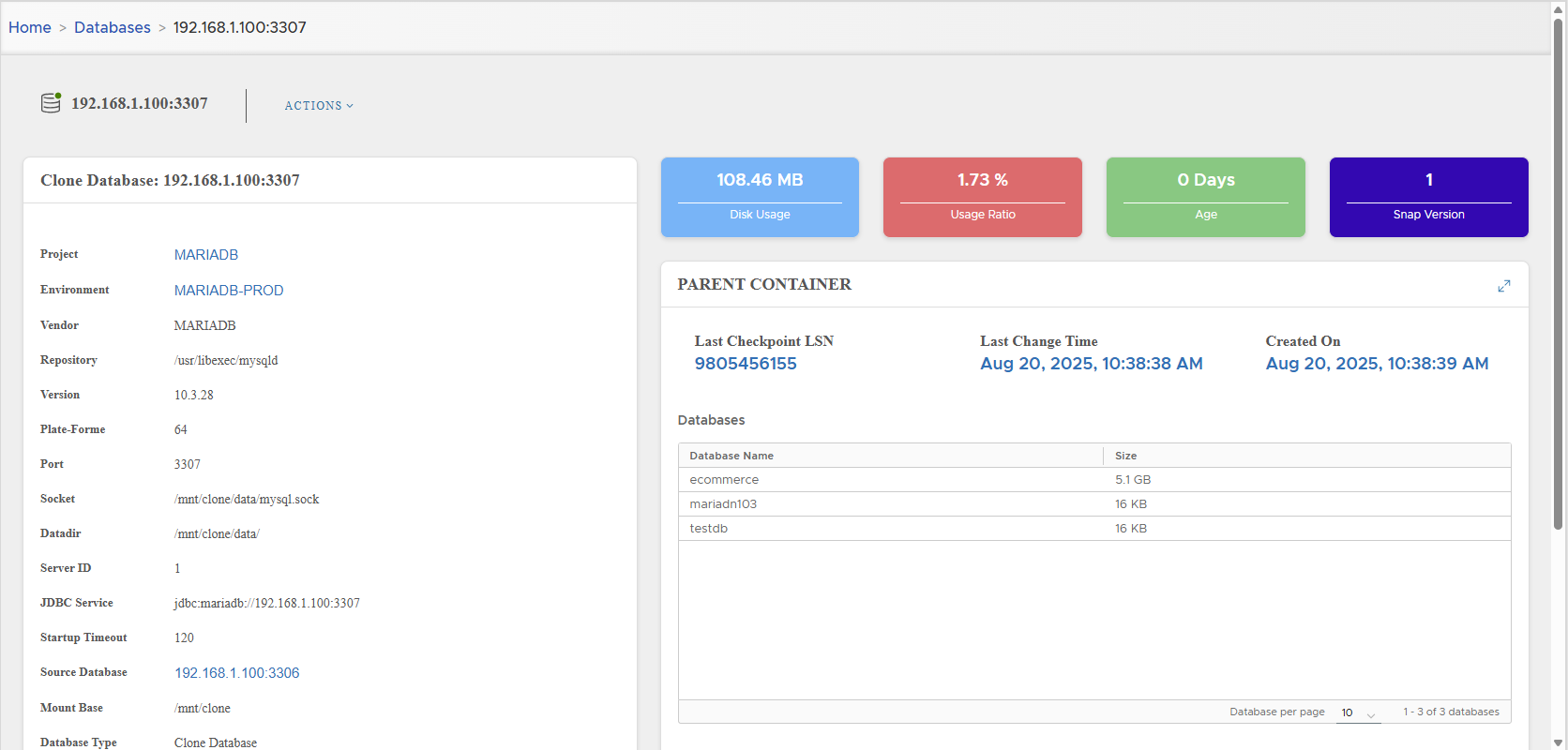
⚡ Virtual clones consume very little disk space compared to the source server.
📋 MariaDB Virtual Clone Management
Configuration Parameters
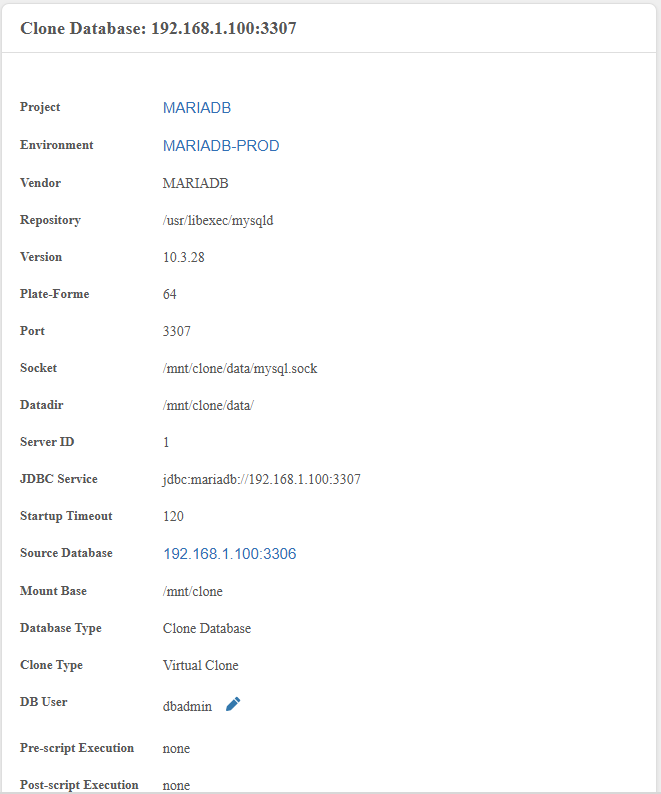
Left side panel displays configuration details:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Project | Project owning the clone |
| Environment | Target environment |
| Vendor | MARIADB |
| Repository | mariadbd binary path |
| Version | MariaDB server version |
| Platform | 32-bit or 64-bit |
| Port | Connection port |
| Socket | Connection socket |
| Datadir | Data directory |
| Server ID | MariaDB server identifier |
| JDBC Service | JDBC connection string |
| Startup Timeout | Timeout before throwing startup error |
| Source Database | Name of source DB server |
| Mount Base | NFS mount point |
| Database Type | Clone Database |
| DB User | Clone DB user |
| Specific Post Script Execution | Status (none, failed, success) |
| Generic Post Script Execution | Status (none, failed, success) |
| Datamasking | Status (none, failed, success) |
| Creation Time | Timestamp of clone creation |
| Created By | User who created the clone |
Dashboard Cards
The right side displays:
- Disk Usage
- Disk Usage Ratio vs live DB
- Clone Age
- Snapshot Version (increments on reset)

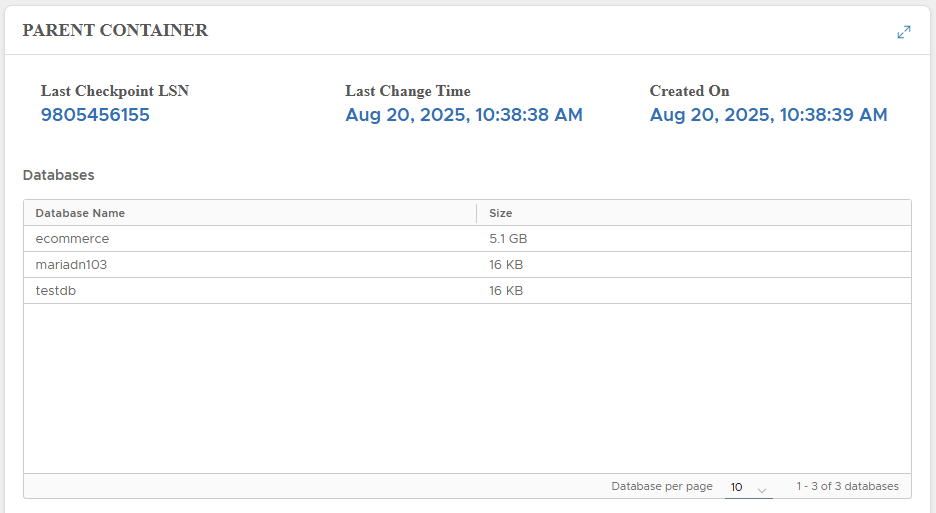
Parent Container
Information about snapshot lineage:
- Last Checkpoint LSN
- Last Change Time
- Parent snapshot creation time
- List of parent schemas
🔑 Changing Database Credentials
- Click pencil icon near DB User.
- Enter new username/password.
- Click VALIDATE.

⚡ Actions on MariaDB Virtual Clones
Actions available under Actions menu:
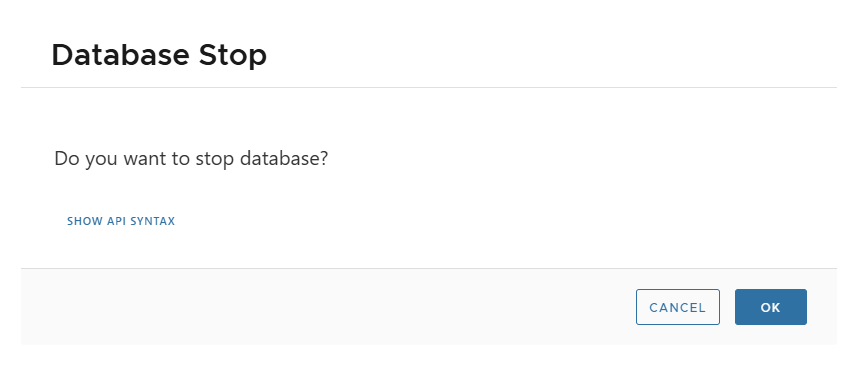
⏹ Stop
- Shuts down MariaDB process.
- Unmounts NFS from host.
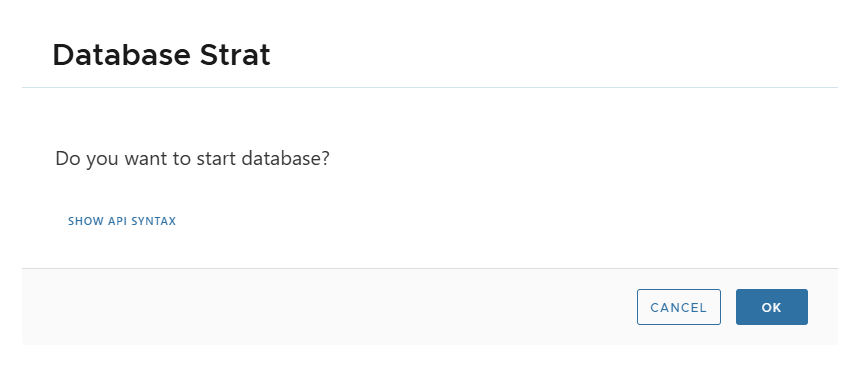
▶️ Start
- Mounts NFS and starts MariaDB process.
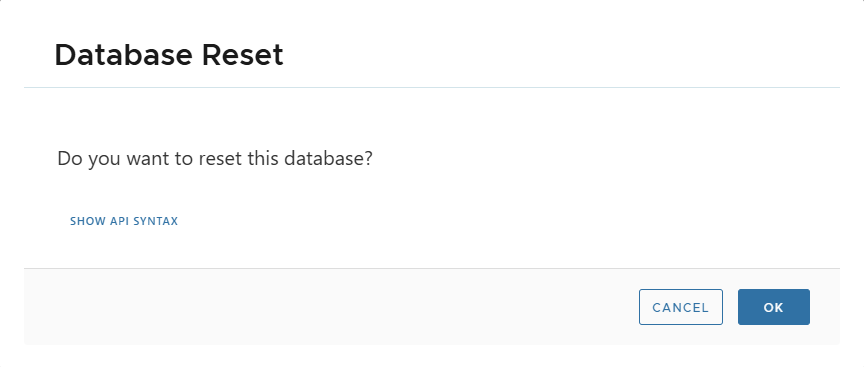
🔄 Reset
- Resets clone to initial state.
- Changes since creation are discarded.
- Snapshot version increments.
🤝 Share
- Creates another clone on same/new environment.
- Very fast (no masking/post-scripts executed).
Steps:
- Actions > Share → Confirm.
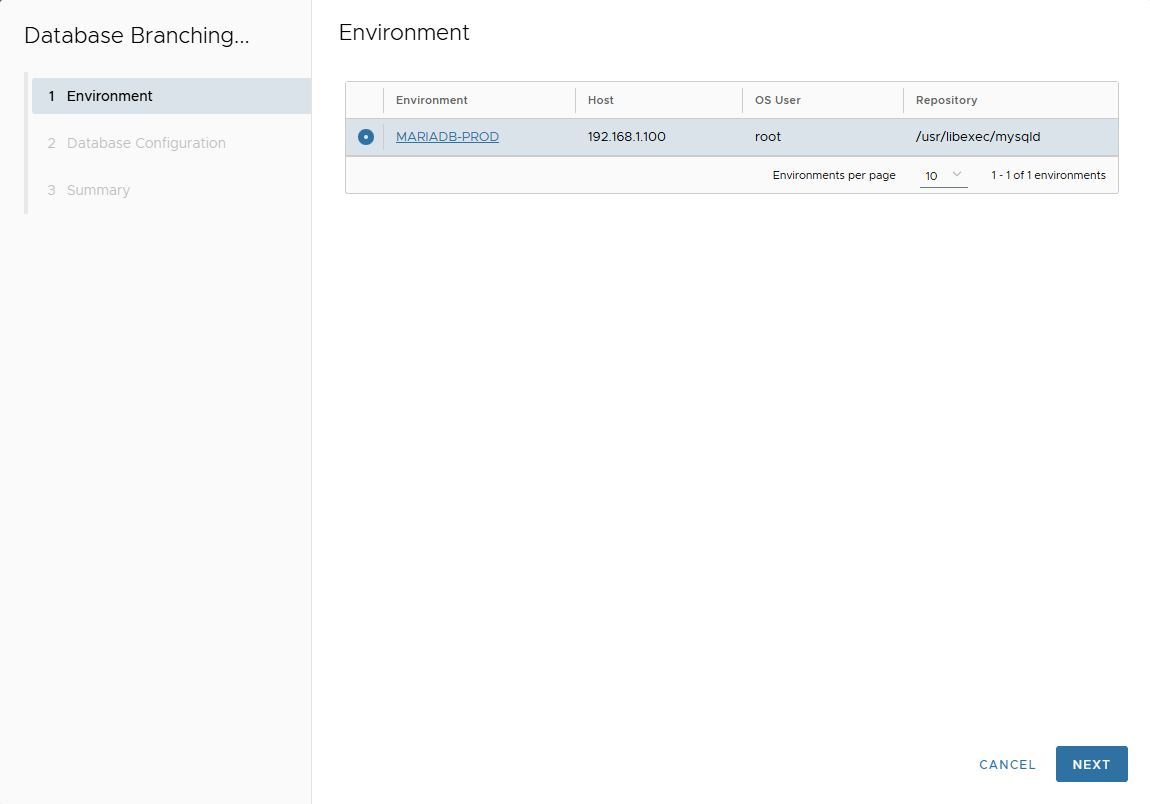
- Select target environment.
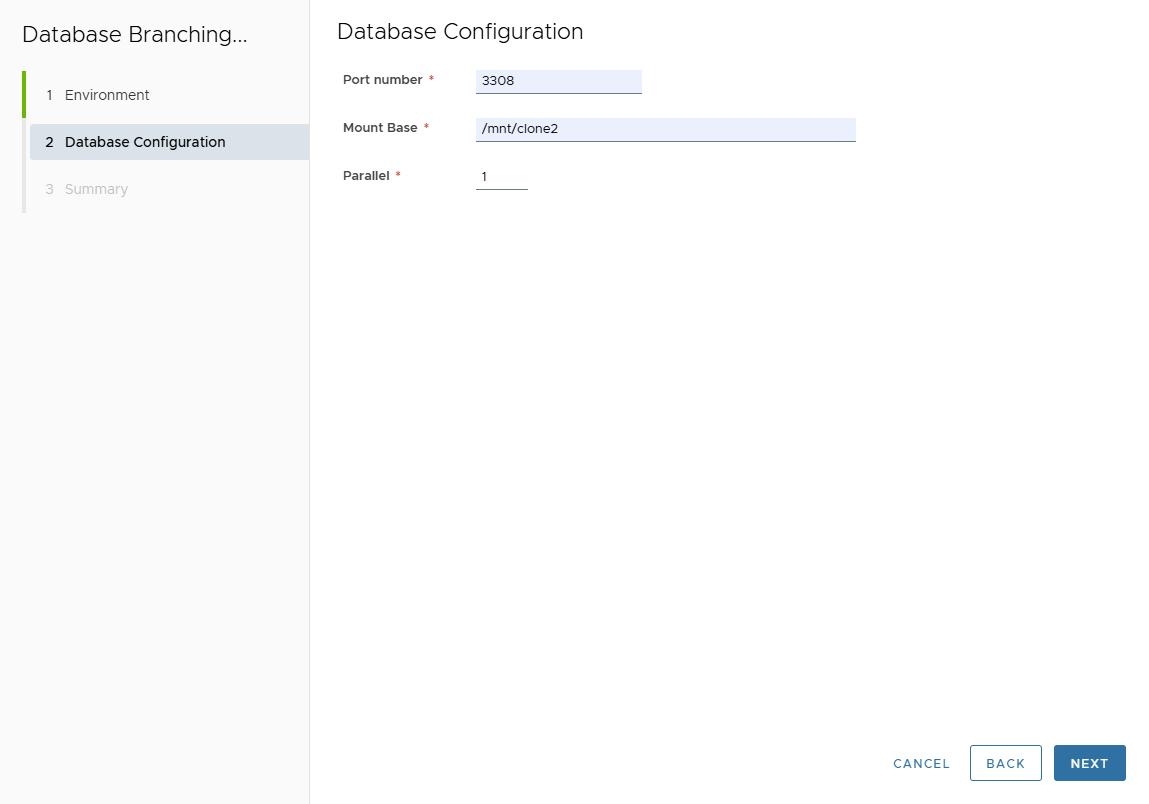
- Enter:
- Port Number
- Mount Base
- Parallel Threads
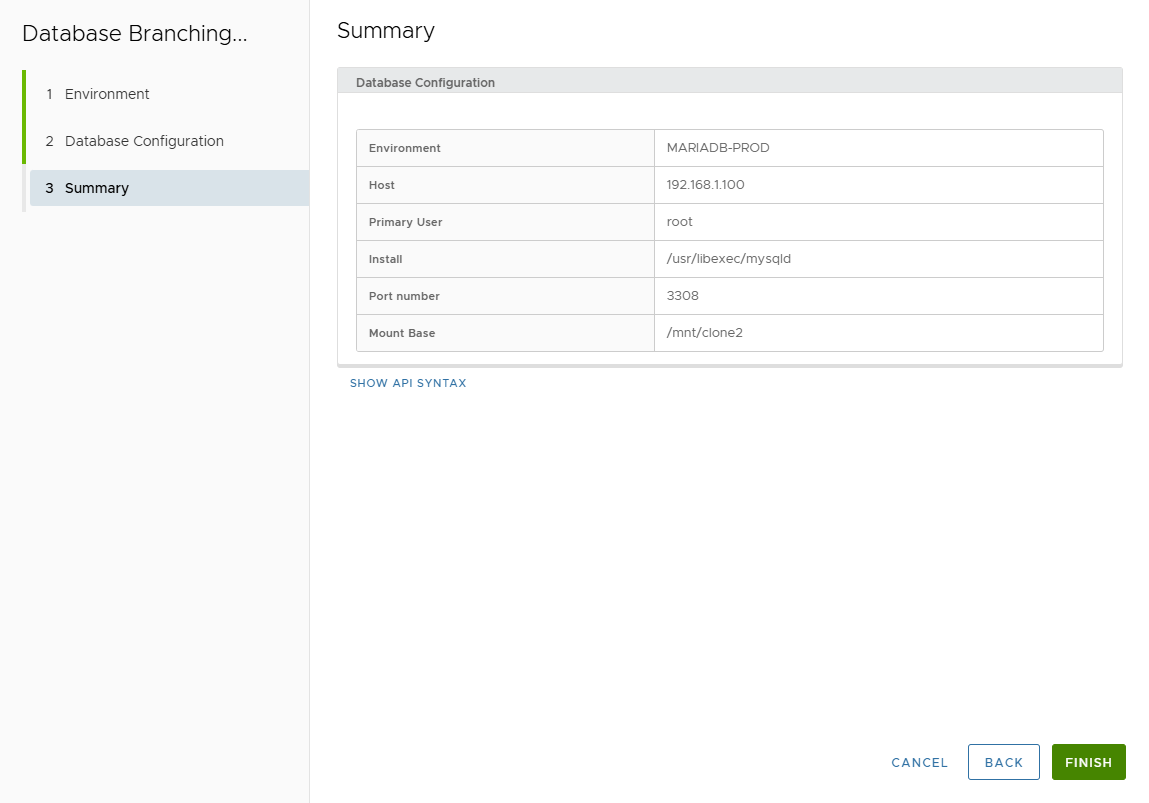
- Review Summary → Finish.
- Track execution progress.
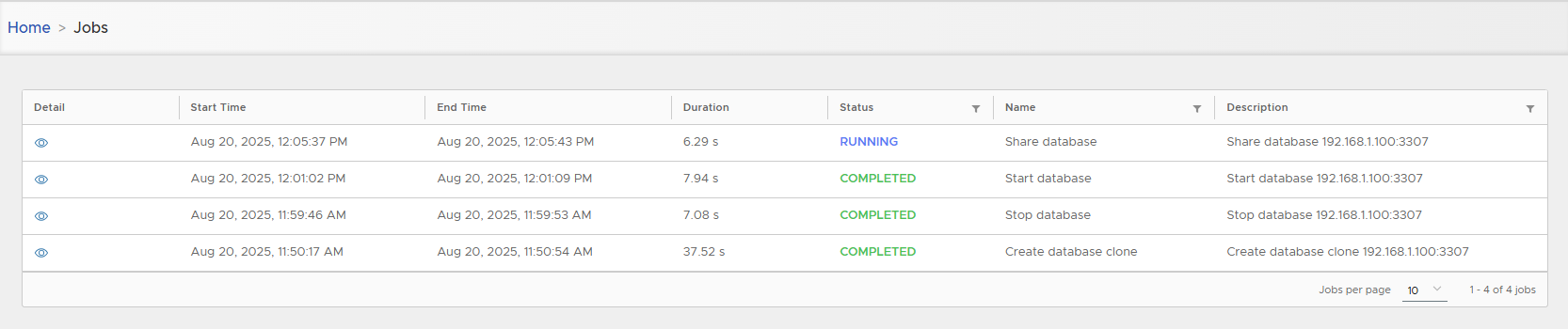
- Shared clone appears in clone list.
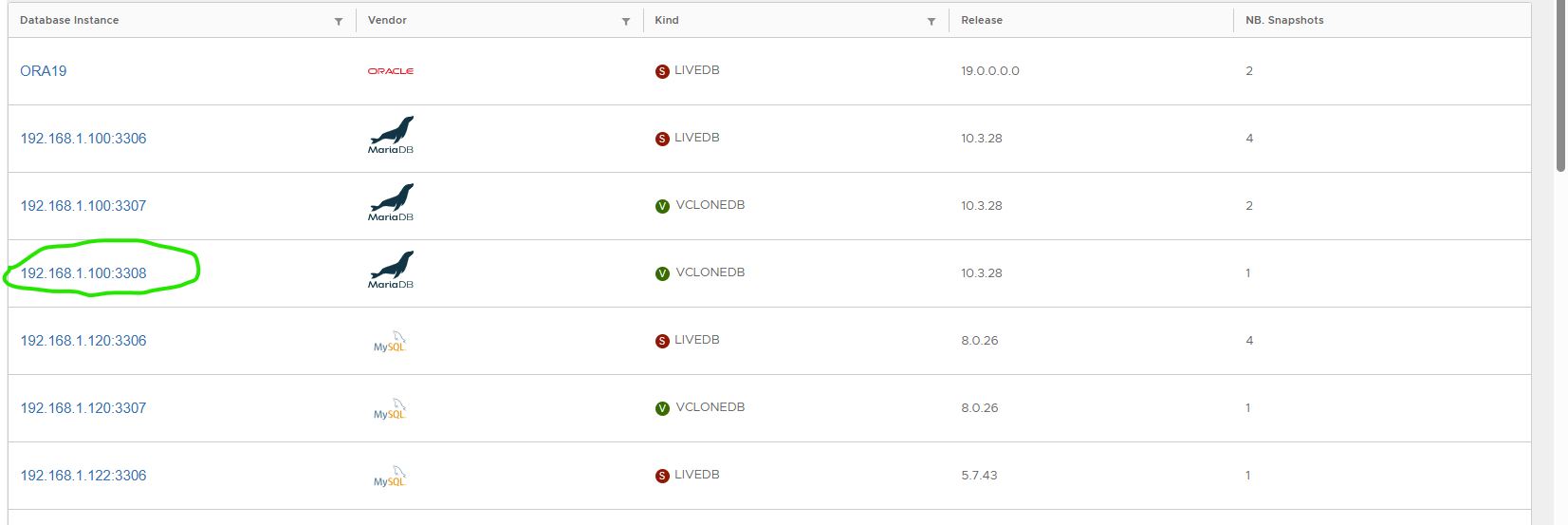
💽 Convert to Physical
- Converts virtual clone to physical (copies DB files locally).
- Requires enough disk space (same as source).
Steps:
- Actions > Convert to Physical → Confirm.
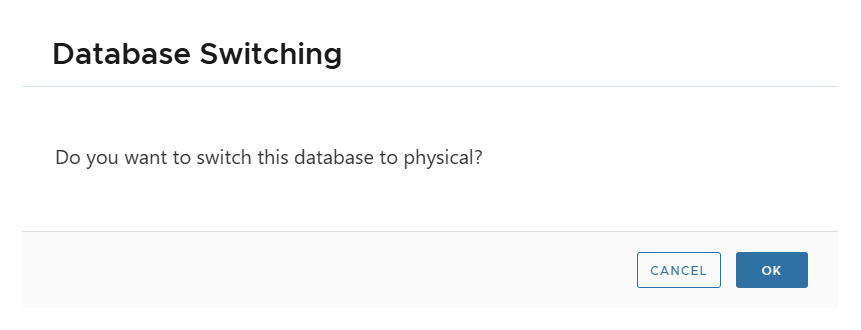
- Enter Local Directory on target host.
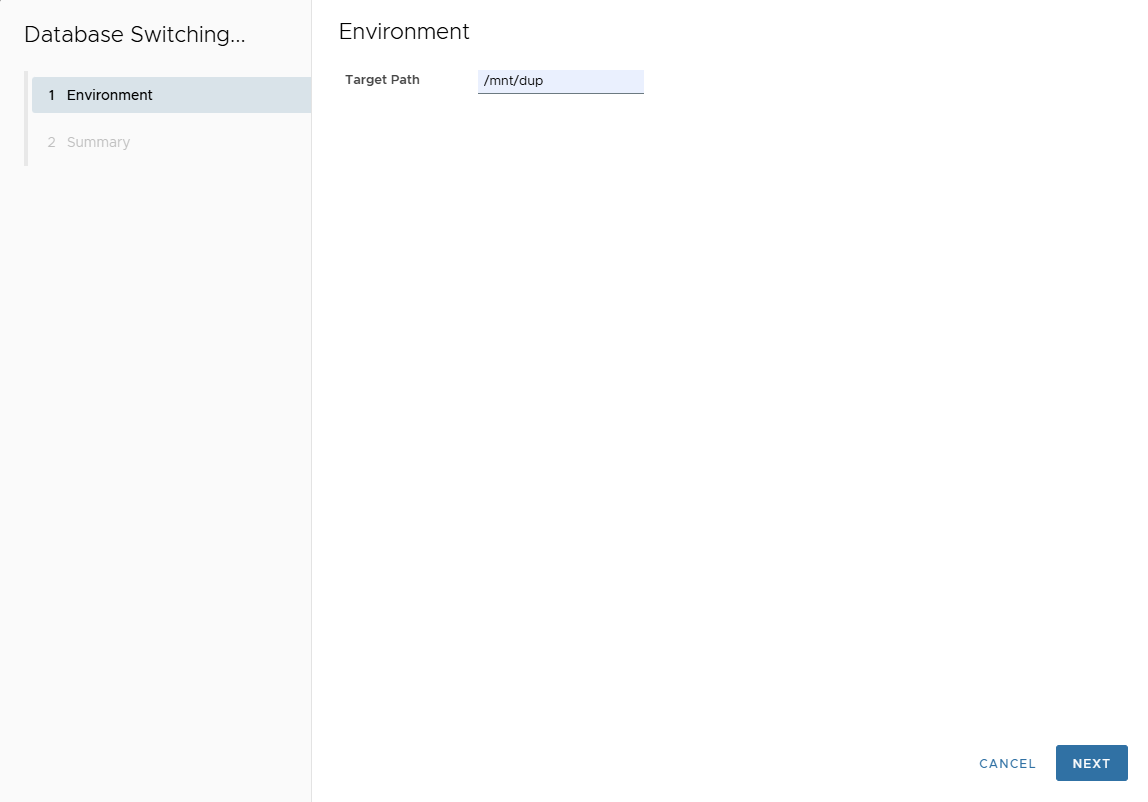
- Review Summary → Finish.
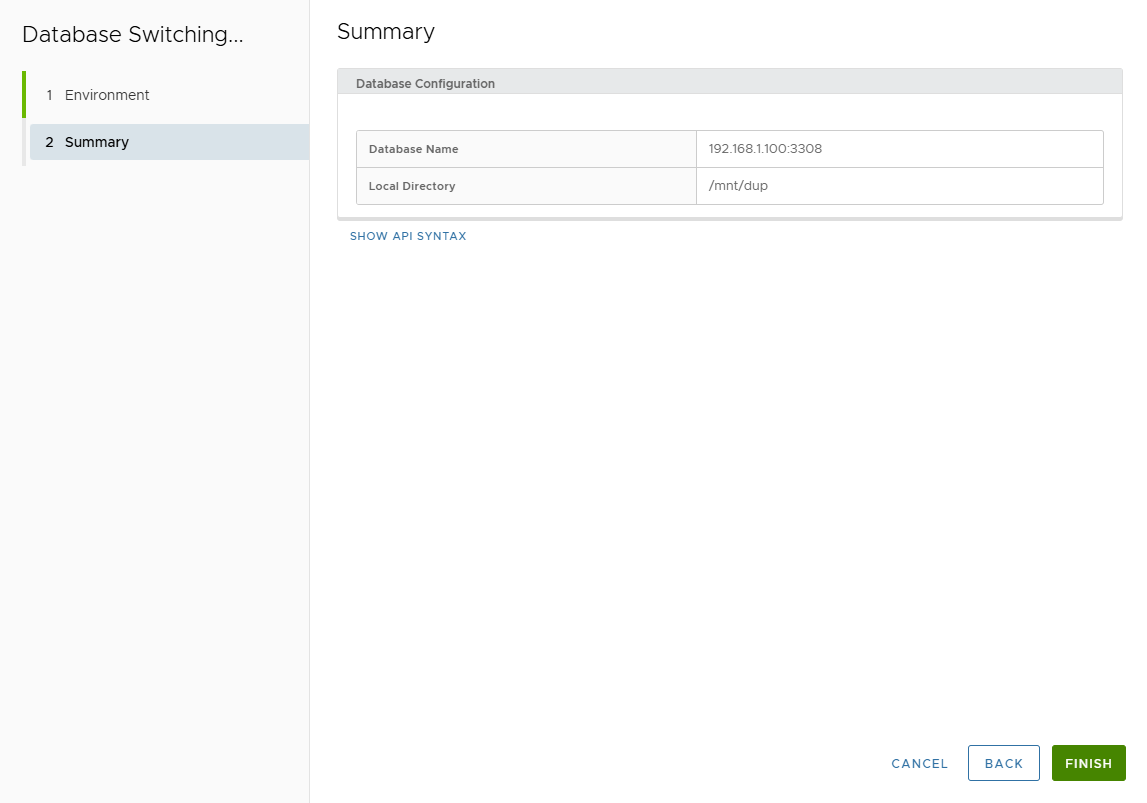
- Track job progress.
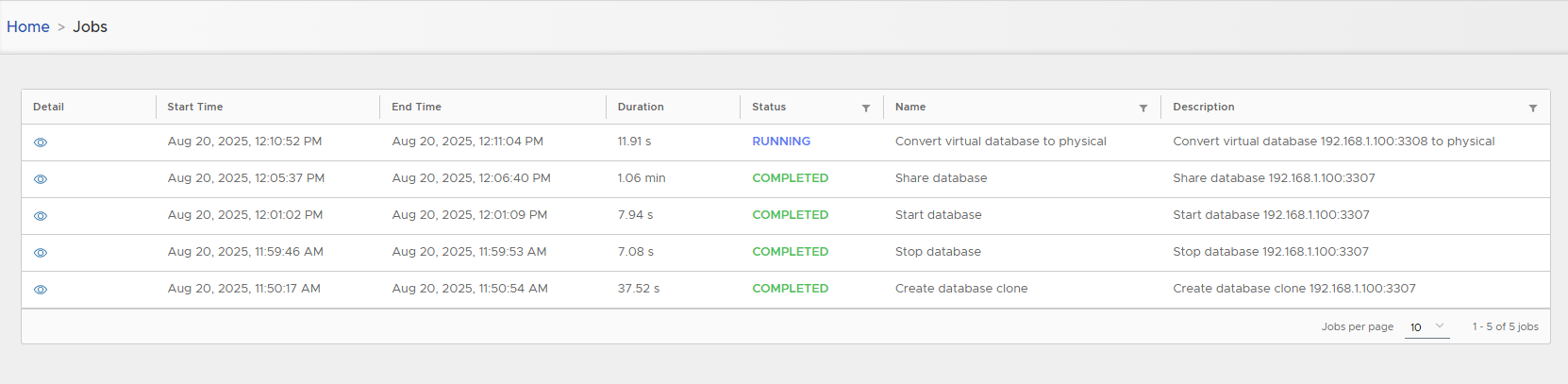
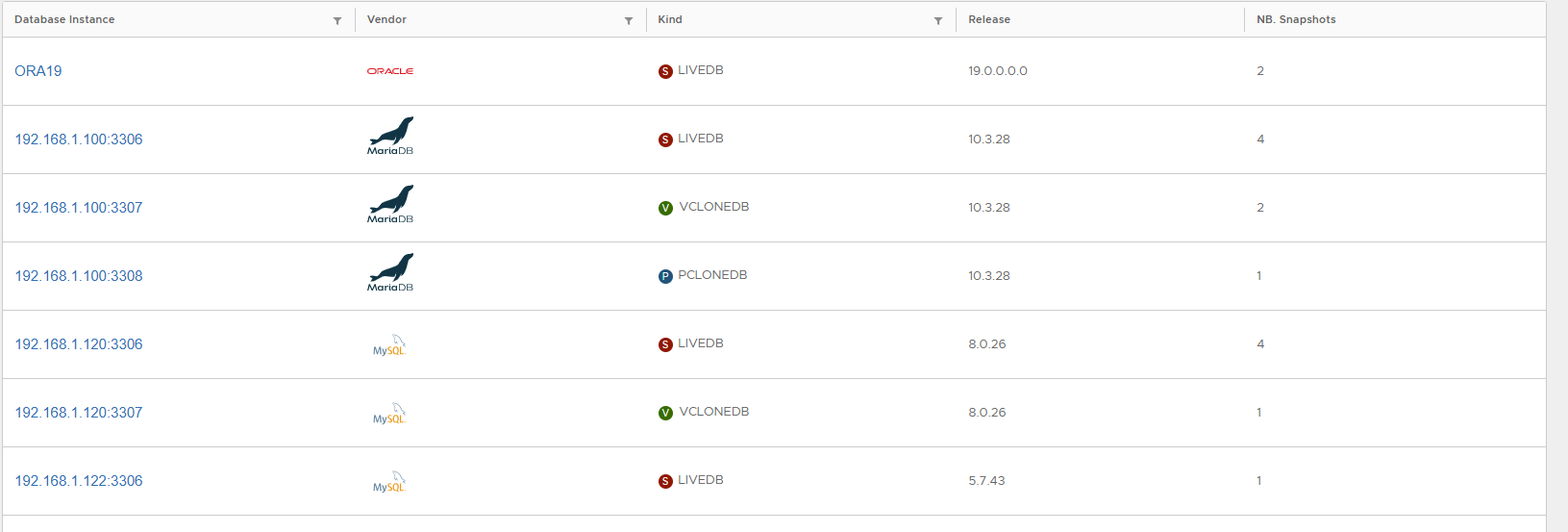
- Converted clone is tagged as Physical.
The database duplication script automatically detects if the parallel command is available on your system:
- With parallel installed: Database files will be copied concurrently based on the parallel degree specified.
- Without parallel: Files will be copied sequentially (one by one), which takes considerably longer.
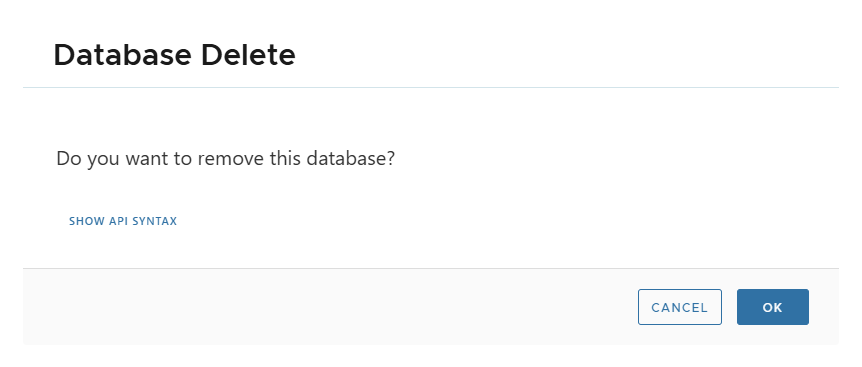
🗑 Delete
- Deletes virtual clone metadata from XLServer.
- Confirmation required.
🏗️ Create MariaDB Physical Clone
-
Open MariaDB database detail page.
-
Click Actions > Create Physical Clone → Confirm.
-
Cloning wizard appears.
-
Select Target Environment → Next.
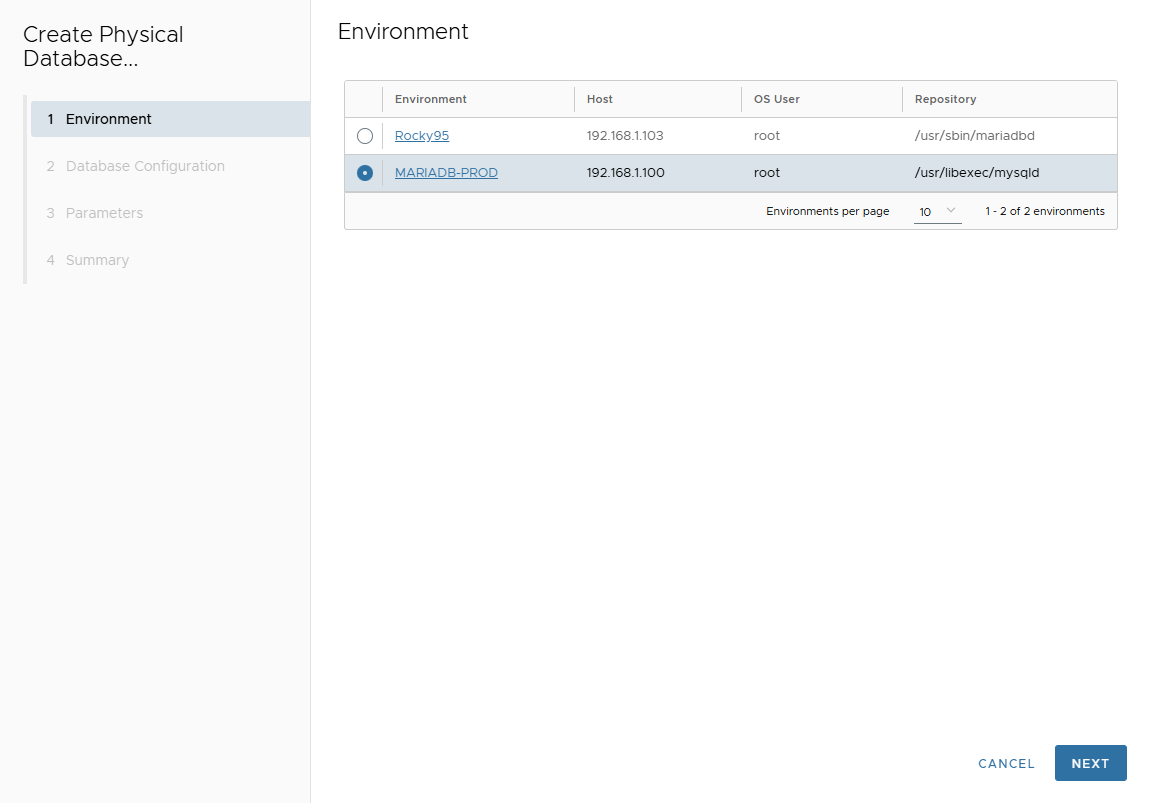
-
On Database Configuration page, enter:
- Port Number
- Mount Base
- Post Script Path (optional)
- Parallel threads
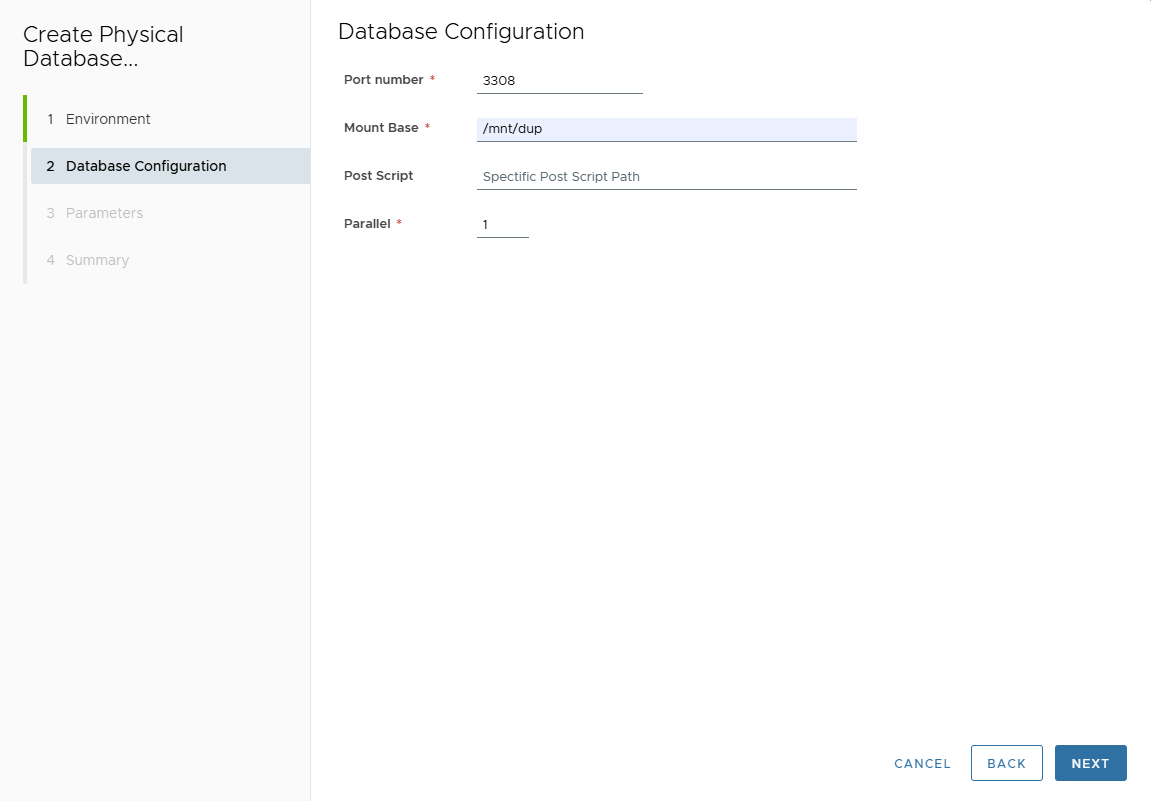
-
In Parameters page, adjust parameters.
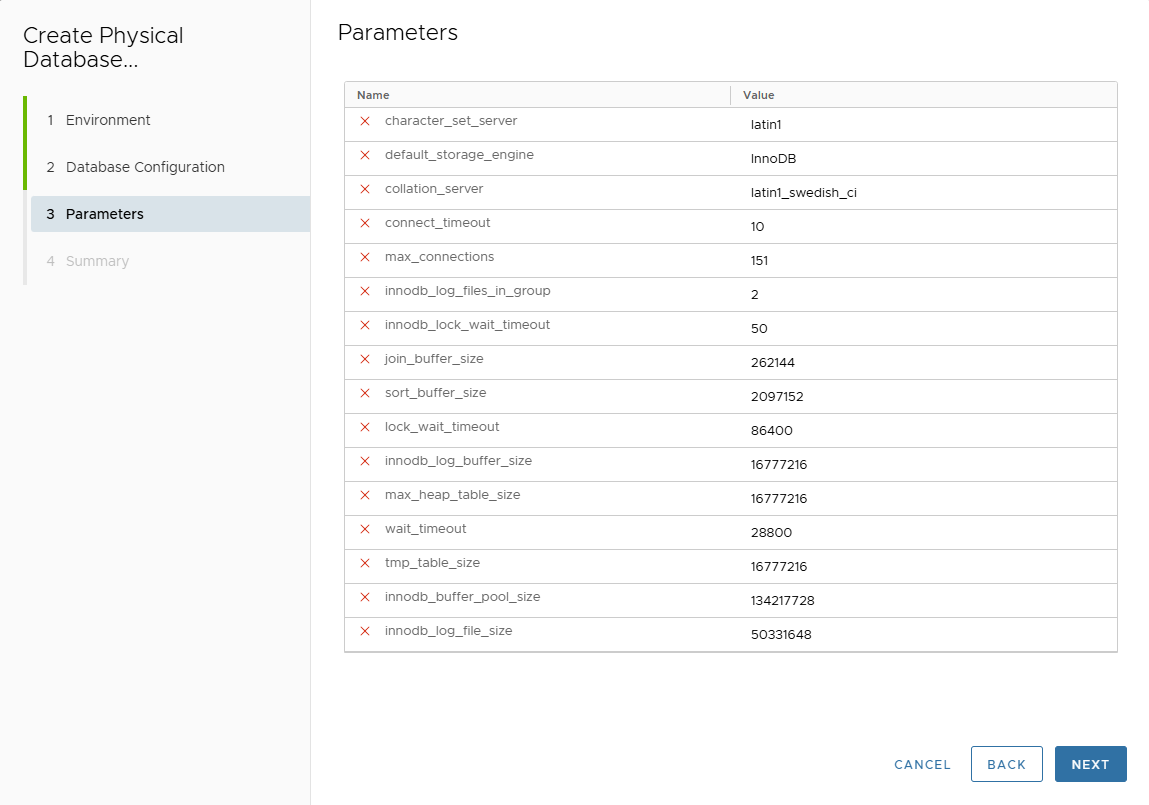
-
Review Summary page.
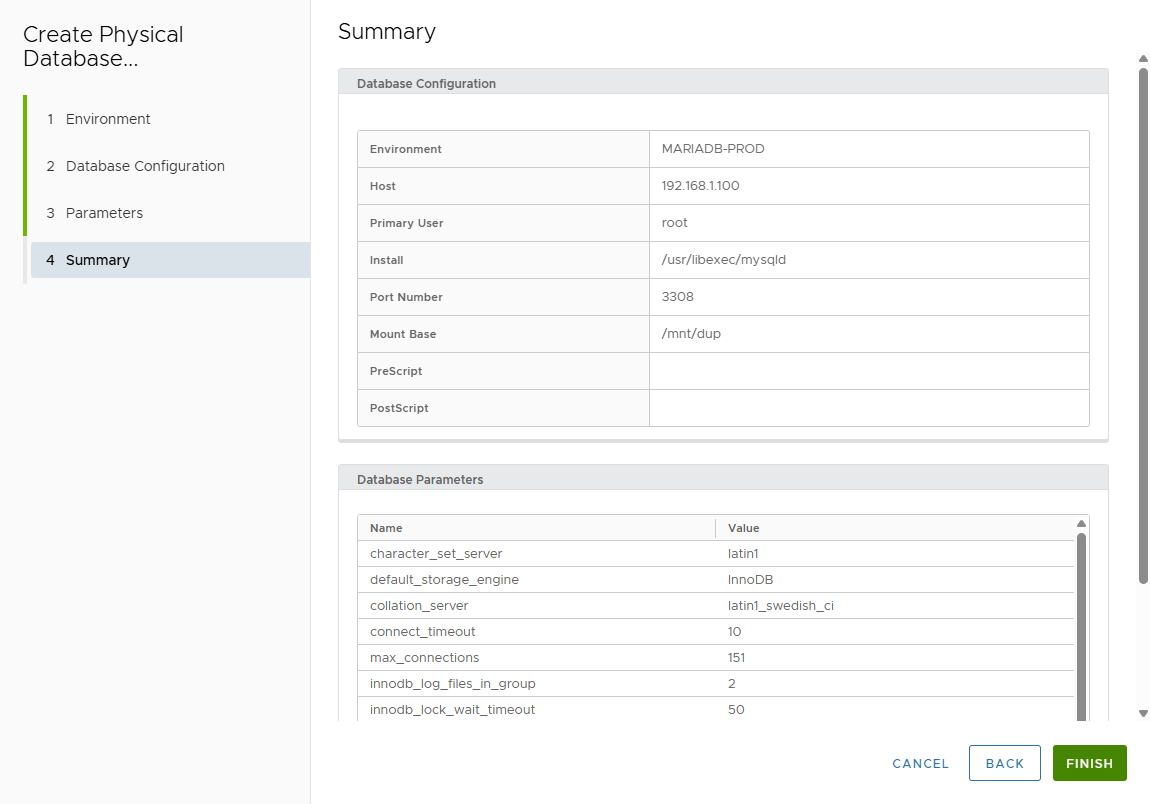
-
Click FINISH.
-
Track job execution.
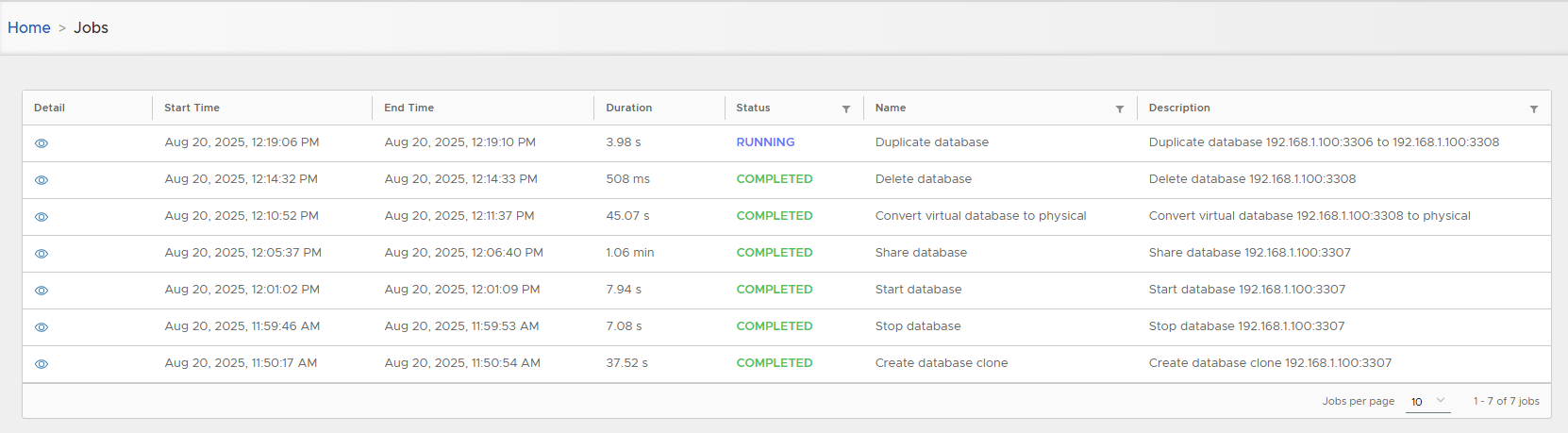
Physical clones take time depending on source DB size.
-
Metadata appears in detail page.
Physical clones have no container in XLServer.
The database duplication script automatically detects if the parallel command is available on your system:
- With parallel installed: Database files will be copied concurrently based on the parallel degree specified.
- Without parallel: Files will be copied sequentially (one by one), which takes considerably longer.
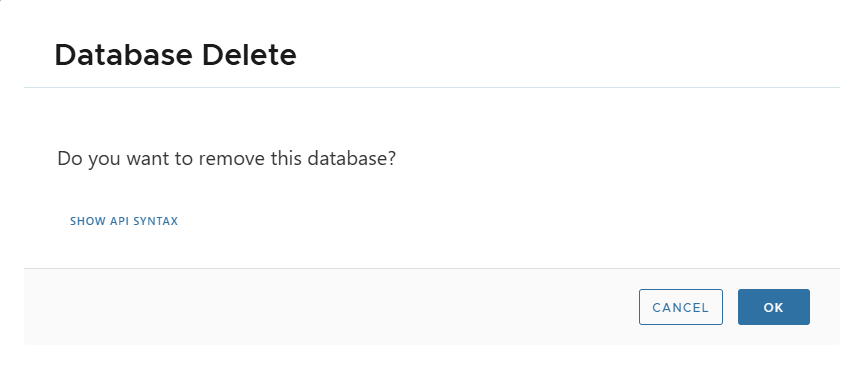
🗑 Delete Physical Clone
- Actions > Delete.
- Removes clone metadata from XLServer only.
- Running database continues independently.
✅ Summary
- Virtual Clones: Quick, lightweight, minimal storage, easily reset or shared.
- Physical Clones: Full, independent MariaDB servers, resource-intensive, slower to provision.
- Both types provide safe, isolated environments without impacting production.